Effect of glycine-NaOH buffer solution concentration (a) and pH value... | Download Scientific Diagram

Cu extraction after 72 h of leaching by glycine + NaOH (Gly:Cu = 4:1),... | Download Scientific Diagram

Figure S3. (a) Fluorescence spectra obtained in Glycine-HCl-NaOH buffer... | Download Scientific Diagram

What is the product obtained when glycine hydrochloride reacts with two equivalents of NaOH ? Wr... - YouTube

SOLVED: Use the graph below (titration of glycine with NaOH) to answer the following questions: glycine 12.0 10.0 20.0 0.0 0 5 Complete figure axes: Name the X-axis: Volume of NaOH (mL)

SOLVED: Use the graph below (titration of glycine with NaOH) to answer the following questions: glycine 12.0 10.0 20.0 0.0 0 5 Complete figure axes: Name the X-axis: Volume of NaOH (mL)
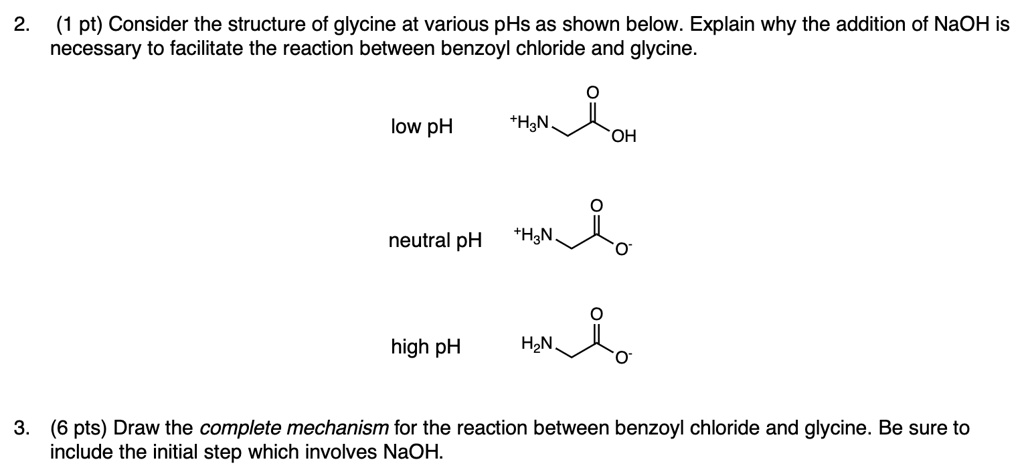
SOLVED: Consider the structure of glycine at various pHs as shown below: Explain why the addition of NaOH is necessary to facilitate the reaction between benzoyl chloride and glycine. low pH tHAN

Show the reaction of the zwitterion of glycine with one equivalent of NaOH to form the basic form. | Homework.Study.com
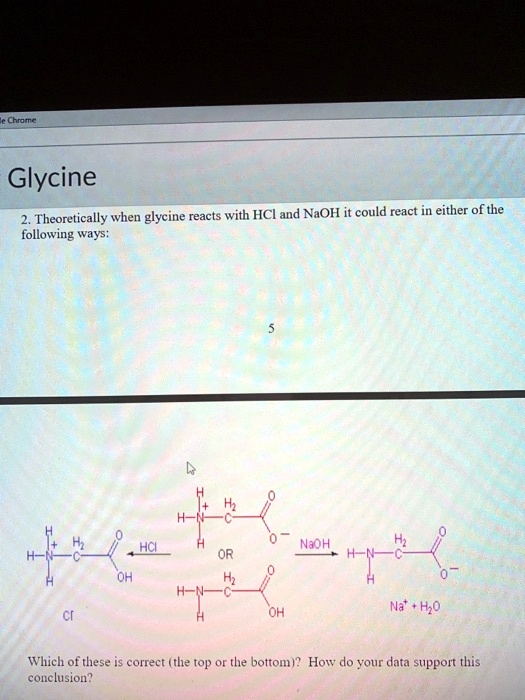
SOLVED: Glycine 2, Theoretically, when glycine reacts with HCl and NaOH, it could react in either of the following ways: HCl + NaOH -> NaCl + H2O Which of these is correct (

Amino acids such as glycine are the building blocks of large molecules called proteins that give structure to muscle, tendon, hair, and nails. What product is formed when glycine is treated with
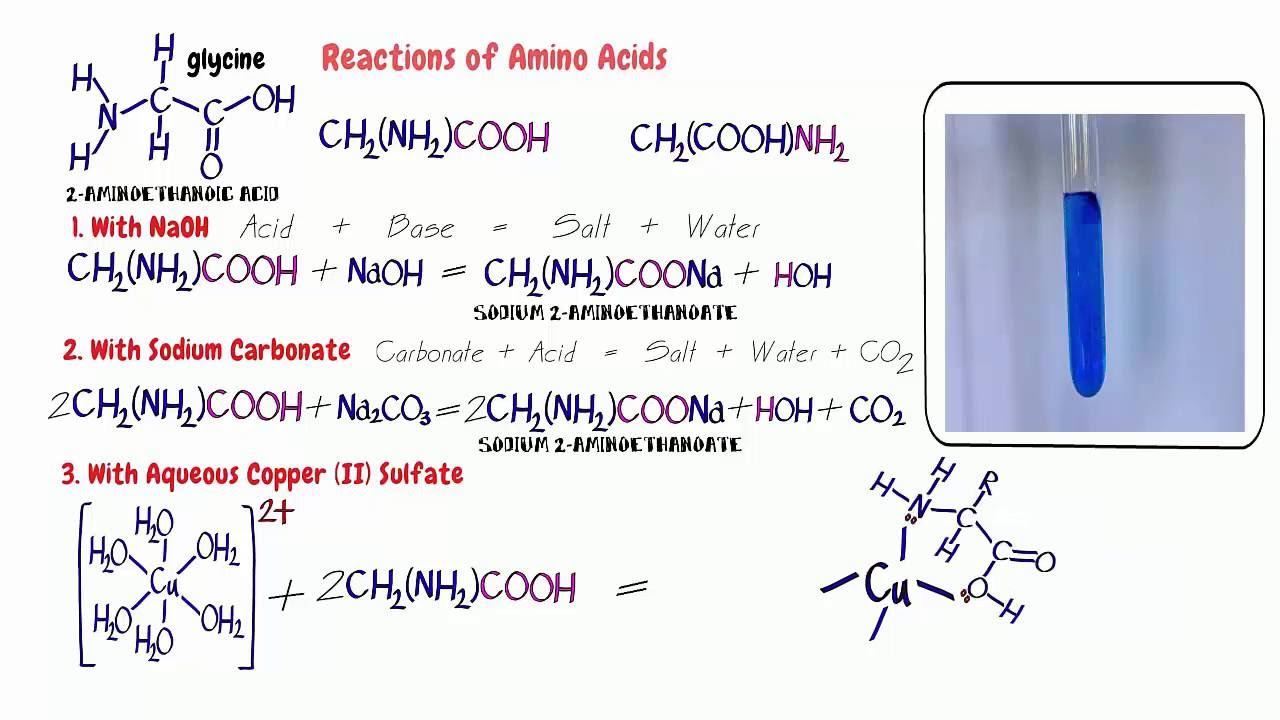
Amino Acids 3. Reactions with sodium hydroxide, sodium carbonate & copper (II) sulfate solution. - YouTube

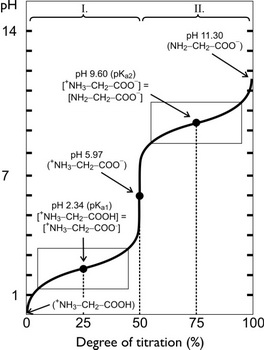
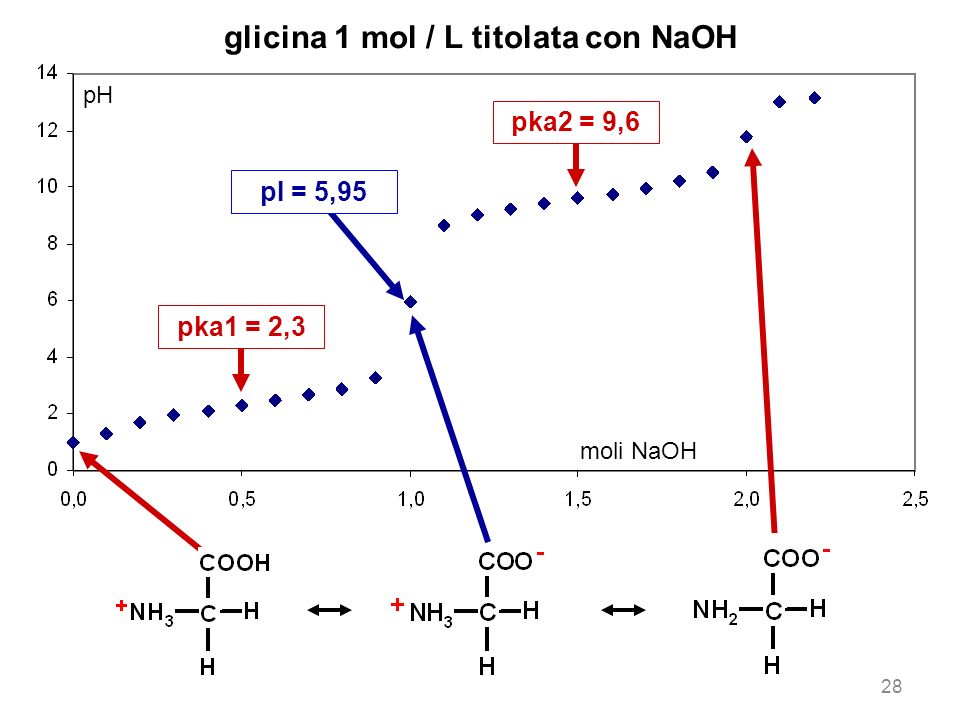
Determinazione del punto isoelettrico della glicina attraverso la titolazione potenziometrica - Studocu

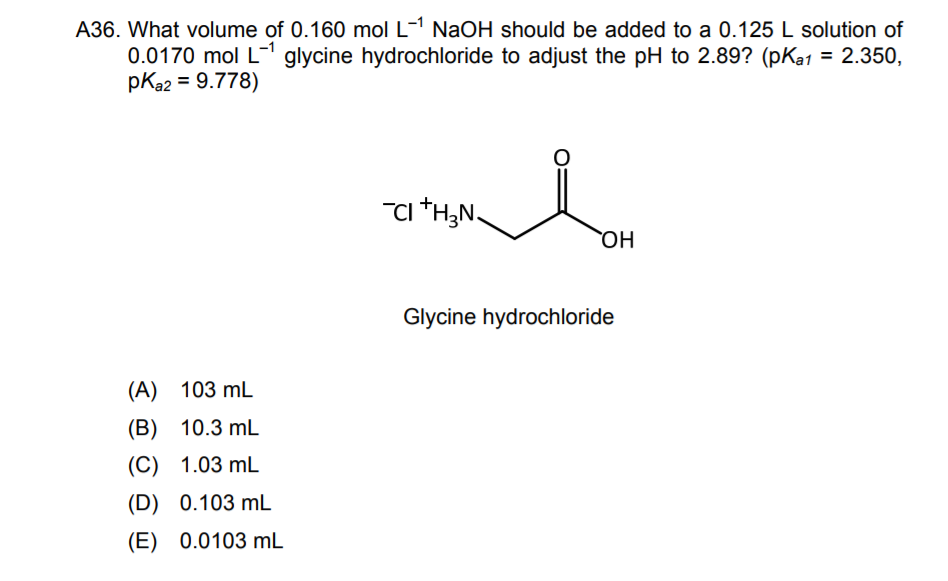
A buffer using the amino acid glycine is prepared by mixing 80 ml of 1.0M glycine, pH 0.5 (i.e. fully protonated), 55 ml of 2M NaOH and 365 ml of water. Calculate
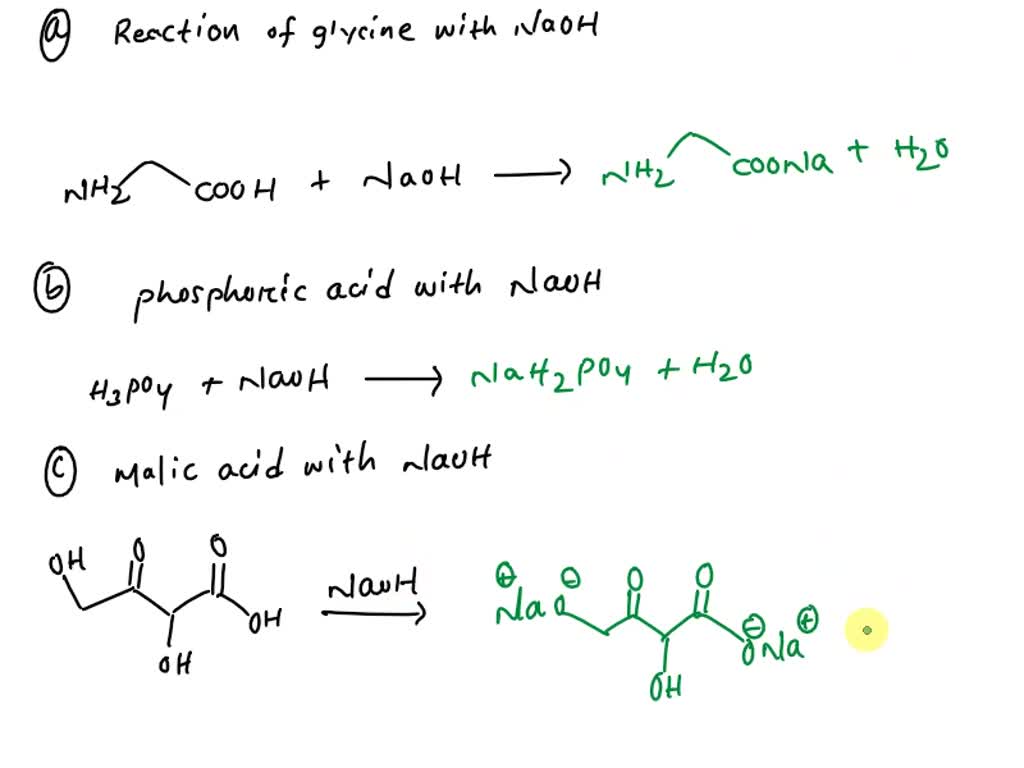
SOLVED: 14. Write the complete reaction of: a. Glycine with NaOH –> b. Phosphoric acid with NaOH –> c. Malic Acid with NaOH –> d. Acetic acid with NaOH –> e. Hydroxylamine with NaOH –>